Exploring Core Islamic Beliefs and Practices
Islam, a faith embraced by over a billion people worldwide, is built upon foundational beliefs and practices that guide the daily lives of its followers. Understanding these core elements offers insight into the spiritual and moral framework that shapes the Muslim community.
The Six Pillars of Iman
At the heart of Islamic belief are the Six Pillars of Iman (faith), which every Muslim is expected to uphold:
- Belief in Allah (Tawhid): Recognizing the oneness of Allah as the sole creator and sustainer of the universe.
- Belief in Angels: Acknowledging the existence of angels who carry out Allah's commands.
- Belief in Divine Books: Accepting the holy scriptures revealed to various prophets, with the Quran being the final and unaltered word of Allah.
- Belief in the Prophets: Honoring the prophets sent by Allah to guide humanity, including figures like Moses, Jesus, and Muhammad (peace be upon them).
- Belief in the Day of Judgment: Anticipating a day when all individuals will be held accountable for their deeds.
- Belief in Qadar (Divine Predestination): Understanding that everything occurs by Allah's will and divine decree.
These pillars collectively form the foundation of a Muslim's faith and worldview.
The Significance of the Quran

Central to Islamic practice is the Quran, considered the literal word of Allah as revealed to Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him). It serves as a comprehensive guide, addressing aspects ranging from spirituality to social justice. Muslims turn to the Quran for guidance in all facets of life, striving to align their actions with its teachings.
Fasting Beyond Ramadan
While Ramadan is the most well-known period for fasting, Islam encourages additional fasting throughout the year. These voluntary fasts, such as those on Mondays and Thursdays or the six days of Shawwal, offer spiritual benefits like increased piety and self-discipline. Physically, fasting can promote health and well-being and many benefits and recommended times are gotten by fasting beyond Ramadan.
Kindness to Animals in Islam

Compassion extends beyond human interactions in Islam; it encompasses all living beings. Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) emphasized mercy towards animals, teaching that kind treatment of them is a reflection of one's faith. Islamic teachings advocate for the humane treatment of animals, prohibiting cruelty and encouraging kindness.
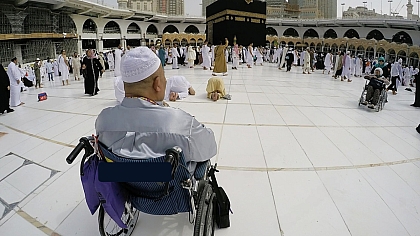
Understanding the Qibla
In Islamic practice, the Qibla refers to the direction Muslims face during prayer, specifically towards the Kaaba in Mecca. This unified direction symbolizes the unity and cohesion of the Muslim community worldwide. Mosques are designed with a mihrab, an architectural feature indicating the Qibla, ensuring worshippers are aligned correctly during prayers.
By embracing these beliefs and practices, Muslims cultivate a life of faith, compassion, and discipline, striving to fulfill their spiritual obligations and contribute positively to society.